Hey folks, welcome back, in this module we are going to talk about What is Network Address Translation (NAT)? It’s working, its advantages, and disadvantages and many more. So, let’s start reading this module and know something amazing.
What is Network Address Translation (NAT)?
Network Address Translation or typically known as NAT is basically made to conserve IP addresses. We need a public IP address to access the internet, but if we are connected to a private network then we can use our private IP address. So, the basic idea of NAT is that it can allow multiple devices to access the internet through a single public address.
Network Address Translation or NAT is the process in which one or more private IP addresses or users connected with local networks are translated into one or more public IP addresses or global networks and vice versa to provide access to the internet to the local hosts.
Many of organizations that want multiple devices to be connected under a single IP address use NAT services.
How does NAT work?
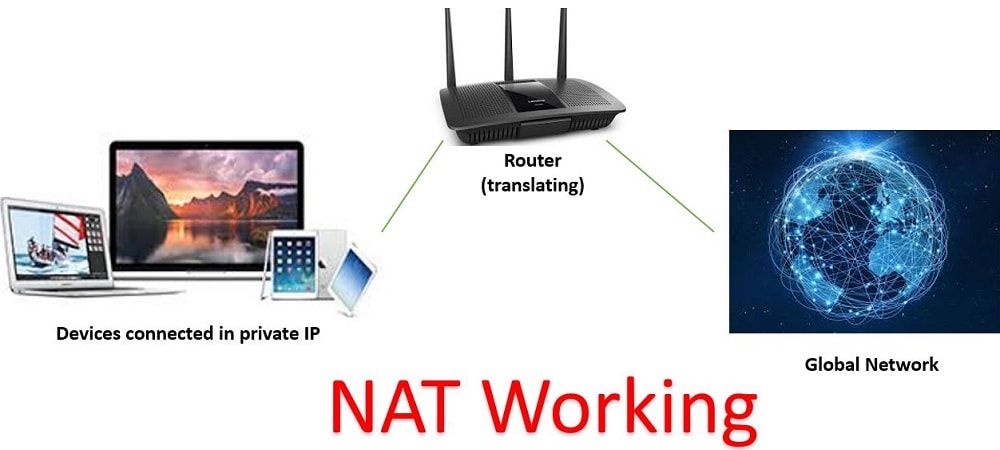
Generally, in basic when NAT is enabled a router is to be configured i.e., the router which has one interface in the global (outside) network and another interface in the local (inside) network and when a packet traverses outside the local i.e., inside the network, then NAT converts that local (private) IP address to a global (public) IP address and vice-versa.
NAT makes devices an agent so that they can work between the internet and the private network and such devices can be a router.
The following below diagram clearly depicts the working of NAT and also shows how the router is been used as an agent between private i.e., local, or public i.e., global networks.
If NAT sometimes runs out of addresses, then i.e., at that time no address is left in the pool to be configured, then the packets will be dropped and at the same time, an Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) host unreachable packet to the destination is sent.
Types of Network Address Translation (NAT)?
There are three different types of NAT available, which are used for different purposes, but the goal is that they work as NAT.
Static Network Address Translation (NAT)
When you move from a local i.e., private unregistered IP address to a global i.e., public registered network, then you must map with the legal public IP address, and this is a one-to-one mapping between global and local address and from this, there will be the public address that will be consistent with the NAT device or the router.
Dynamic Network Address Translation (NAT)
In the previous one, we were switching to the same address, but here the case is totally different in that you don’t have to choose the same IP every time, instead of that it goes through the pool of public IP addresses. Therefore, in this, the router or NAT devices get a new IP address every time when it travels from the private network to the public network.
Port address translation (PAT)
It translates any local or private IP address into a single public IP address. In simple terms, the overloading of NAT is called the PAT. Traffic in the network is distinguished by the different port numbers assigned to them.
So, these are the main three types of network address translation which are having their own use and are designed for different purposes.
Advantages of Network Address Translation (NAT)
Since we have seen a lot about NAT, let’s see some of the advantages of NAT in what sense it can give benefits, or it is useful.
- The legally registered IP address is fully conserved in NAT.
- When the network evolves, it eliminates all the address renumbering.
- One can easily connect to the public network with more flexibility.
- It provides security in terms of providing privacy to the IP address of the device, all the sending and receiving traffic will be hidden.
- Depletion of the IPv4 address is prevented when NAT is enabled.
- The destination addresses and the original address gets hidden, thus this adds additional security to our system and devices.
Disadvantages of Network Address Translation (NAT)
There must be some drawbacks also of the NAT, let’s see some of them that are listed below.
- When NAT is enabled in your device certain applications might not work or might not fully function.
- NAT may result in the delay of the communication of IPv4.
- The router should not tamper with port numbers i.e., transport layers, since it is a network layer device, but it must do so because of the NAT.
- The use of tunnelling is difficult when NAT is enabled on your device.
I hope this module was helpful, and you all must enjoy reading this module about What is Network Address Translation or typically known as NAT. This is the most important and amazing concept that comes under cryptography. For many more amazing modules stay connected with us. Until then Keep learning, Be safe, and Enjoy reading.