In this tutorial, we will deep dive into (Java Database Connectivity) JDBC Architecture in Java Programming. We will learn what JDBC is and know its types in detail. We will also cover JDBC architecture and prerequisites for learning JDBC.
The JDBC Architecture in Java Programming
The term JDBC is an abbreviation for Java Database Connectivity. It is a built-in API available in Java that is used to connect with databases and execute queries. JDBC is specifically available in JavaSE.
Why should I learn JDBC Architecture in Java Programming?
Previously, ODBC API was well-known for database connections and operations. The thing with the ODBC API was that it used the ODBC driver which was written in the C programming language.
The C language is a machine-dependent language and due to this, there was a problem with the compatibility of ODBC drivers. Another important fact is that C is a much-unsecured language compared to Java. These two were the reasons why Java later defined its own API that used JDBC drivers for database connectivity. And the fun fact is that now it is secure because it is written in the Java programming language.
JDBC API can be used to do the following:
- Directly connect to a database
- Creating SQL statements and queries
- Execute queries (with checks) to the database
- Retrieve database objects such as Tables, Indices, etc. from the database.
Prerequisites to learn JDBC Architecture in Java Programming?
To better understand the functionalities of JDBC, you need to have a decent knowledge of Core Java programming in general. This is necessary because it is needed to understand different methods, variables, constants, and classes that work collectively to operate on a database.
A Basic understanding of CRUD operations in a database and SQL is also important to know to learn JDBC. This will help you in making queries and executing them in a database.
JDBC Architecture in Java Programming
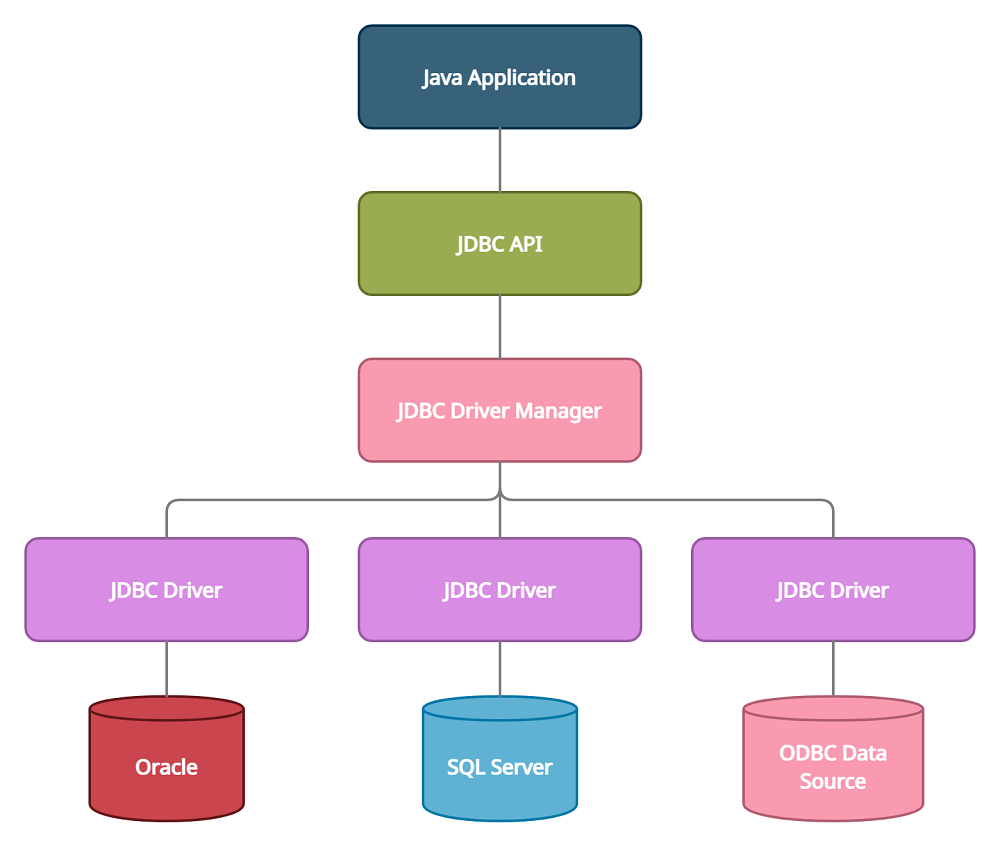
The JDBC Architecture has two layers, they are:
- JDBC API − Provides connection from Application to JDBC Manager.
- JDBC Driver API – Supports the connection between JDBC Manager and the Driver.
JDBC Architecture in Java Programming uses a driver manager and a database-specific driver to connect to a database. The JDBC driver manager makes sure that the correct driver is being used to access the databases. It is also capable of handling multiple drivers connected to multiple databases simultaneously.
Types of JDBC Drivers in Java Programming
There are two packages i.e., java.sql and javax.sql that are known for JDBC connections and executions. Java uses JDBC drivers to connect with any database. They are 4 types –
- JDBC – ODBC Bridge Driver
- Native Driver
- Network Protocol Driver
- Thin Driver
JDBC – ODBC Bridge Driver
In this type of driver, a JDBC bridge is used to access different ODBC drivers that are installed on the client computer. Previously, this was the most famous driver used for database connectivity.
Oracle has stopped its support for the JDBC-ODBC Bridge from Java 8 and above. It also recommends making use of JDBC drivers provided by the vendor of the database instead of the JDBC-ODBC Bridge.
Advantages of JDBC – ODBC Bridge Driver:
- It is easy to use the driver.
- It can be used to connect to any database.
Disadvantages of JDBC – ODBC Bridge Driver
- JDBC calls are converted to ODBC function calls which result in a performance hit.
- ODBC drivers are platform-dependent drivers.
- The client computer needs to have an ODBC driver installed for it to work.
Native Driver
The Native API driver is another driver that uses client-side libraries of the database to make database connections. It is used to convert the JDBC method calls into native calls (C/C++) of the database.
Advantage of Native Driver:
- It is better in flexibility than JDBC – ODBC driver
The disadvantage of Native Driver:
- The driver must be installed on the client computer for it to work.
Network Protocol Driver
In this type of driver, a database is accessed using a 3-layered approach. It uses a middleware server that connects to the database and makes JDBC calls. It connects through vendor-specific protocols.
The standard type of network sockets is used by the client machines to interact with the middleware server. The user sends the database query information to the server and the server translates them into DBMS calls and then forwards it to the database server.
Network Protocol Driver is extremely flexible because it doesn’t require any kind of code or programming on the client and can provide access to multiple databases.
Advantages of Network Protocol Driver:
- It is highly flexible.
- It doesn’t require any special coding to connect to the database.
Disadvantages of Network Protocol Driver
- A constant network is needed to connect to the database.
- The middleware server must be highly configured.
- Performance is a bit low due to indirect database access.
Thin Driver
The thin driver directly converts the JDBC calls made by the program into vendor-specific database protocol. It is also known as a Type 4 driver or Java Based Driver. It uses a socket connection is used to make database connections to the database. It also provides the highest level of performance due to being provided by the vendor itself.
The Thin driver is highly flexible and doesn’t require you to install any kind of special software on the client machine.
Advantages of Thin Driver
- It is highly flexible
- Doesn’t require any kind of special software on the client machine
The disadvantage of Thin Driver
- Provided by the vendor only
I hope you got the most out of this tutorial on JDBC Architecture in Java Programming To learn more content like this in the future, stay in touch with us.